Dee Caulcrick's Blog
Computer Science & Stuff

Understanding Bubble Sort Algorithm
Last Updated: January 25, 2024
Sorting algorithms play a crucial role in computer science, and one of the simplest among them is the Bubble Sort algorithm.
What is Bubble Sort?
Bubble Sort is a simple sorting algorithm that repeatedly steps through a list (or array), compares adjacent elements, and swaps them if they are in the wrong order. This process is repeated until the entire list is sorted in ascending order. It derives its name from the way smaller elements "bubble" to the top of the list with each iteration.
How does it work?
Let's visualize how the Bubble Sort algorithm works:
Imagine you have an unsorted array: [ 8, 4, 3, 2].
Pass 1:
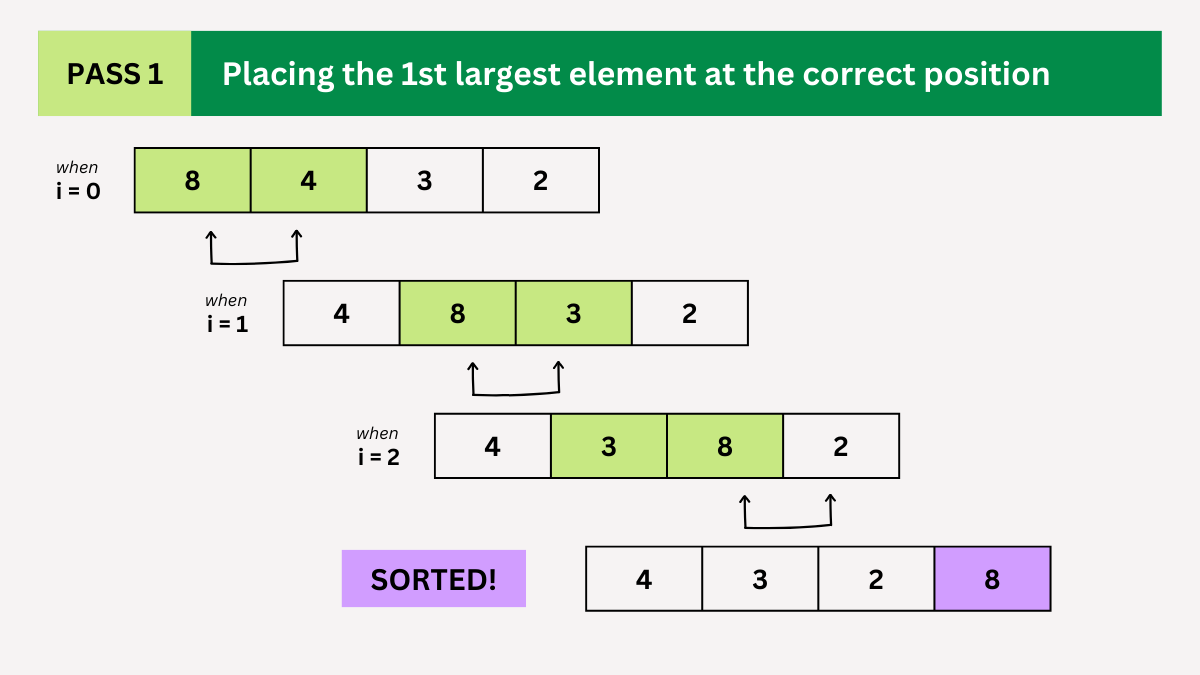
- Compare the first two elements: 8 and 4. Since 8 > 4, swap them. Now the array becomes [4, 8, 3, 2].
- Compare 8 and 3. Since 8 > 3, swap them. Now the array becomes [4, 3, 8, 2].
- Compare 8 and 2. Since 8 > 2, swap them and the resulting array is [4, 3, 2, 8]. The largest element (8) is now at the end of the array.
Pass 2:
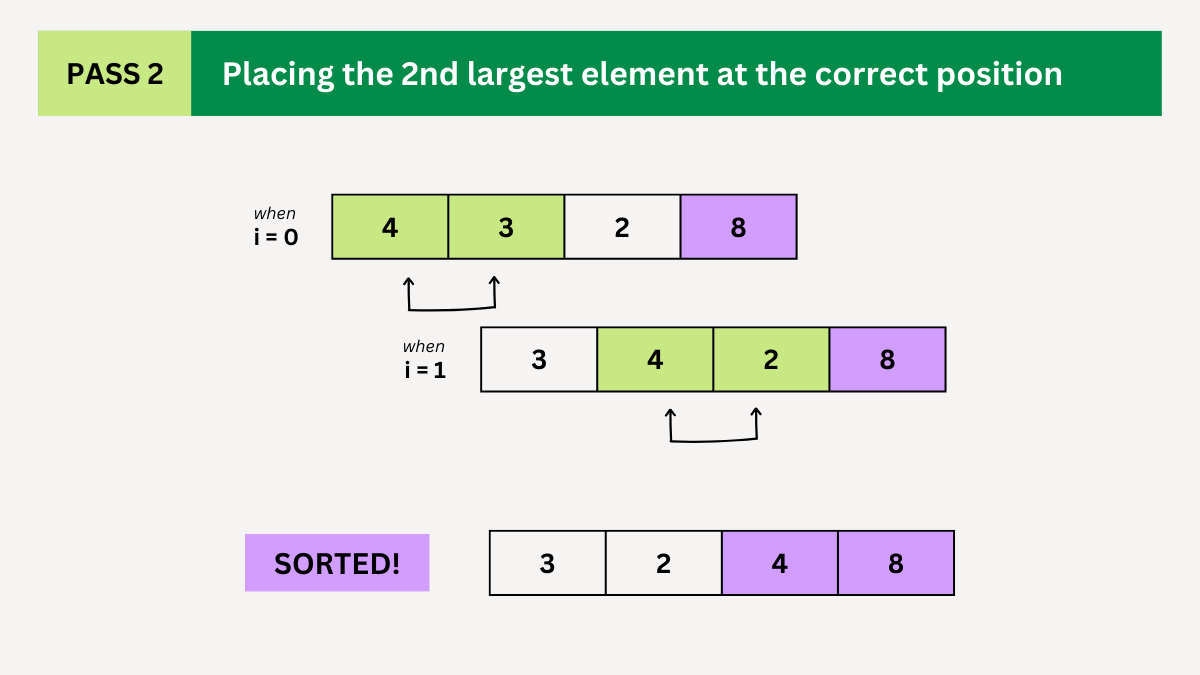
- Repeat the process but exclude the last element (8), which is already in its correct position.
- Compare 4 and 3. Since 4 > 3, swap them. The array becomes [3, 4, 2, 8].
- Compare 4 and 2. Swap them, resulting in [3, 2, 4, 8].
- The second largest element is now in its correct position.
Pass 3
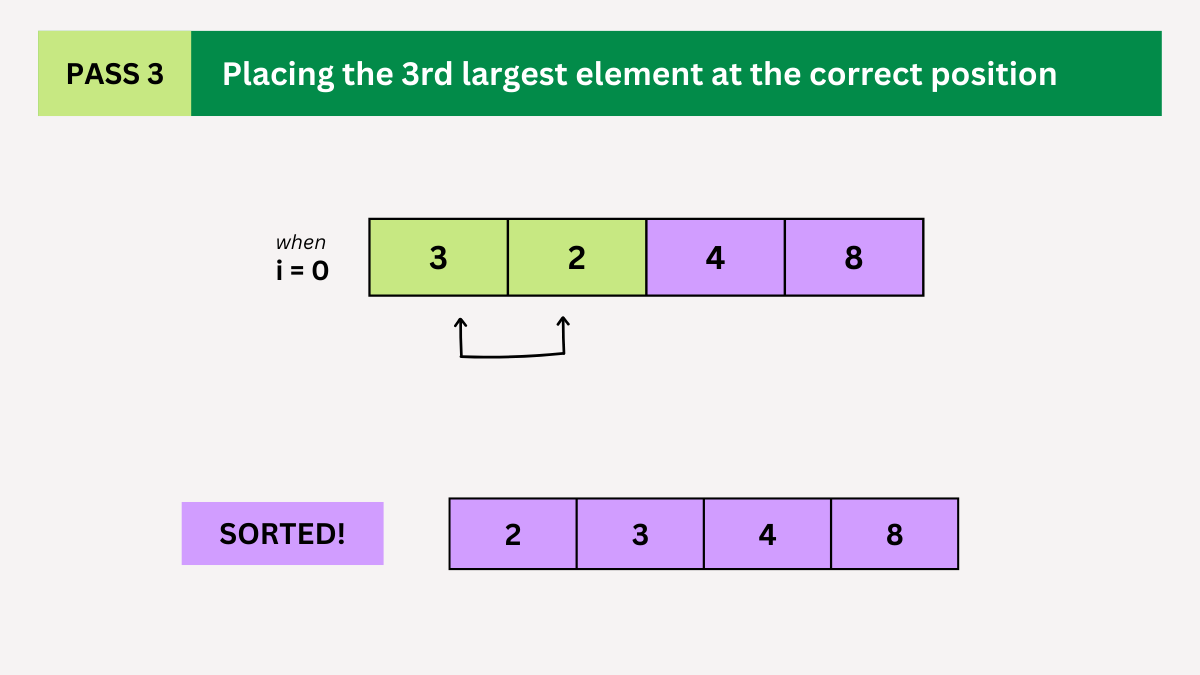
- Repeat the process but exclude the last two elements which are already in their correct position.
- Compare 3 and 2. Swap them. The sorted array is now [2, 3, 4, 8]
Observation
Total no. of passes = n-1
Total no. of comparisons = n*(n-1)/2
Step-by-Step Implementation in JavaScript:
Let's delve into the step-by-step implementation of the Bubble Sort algorithm in JavaScript:
Step 1: Define the Bubble Sort function:
First, define a function named bubbleSort that takes an array arr as a parameter. We also declare two variables:
lento store the length of the array andswappedto track whether any swaps were made during a pass through the array.
javascriptfunction bubbleSort(arr) { let len = arr.length; let swapped;
Step 2: Implement the Sorting Logic:
javascriptdo { swapped = false; for (let i = 0; i < len - 1; i++) { //cheeck if the current element arr[i] is greater than the next element arr[i + 1] if (arr[i] > arr[i + 1]) { //swap values let temp = arr[i]; arr[i] = arr[i + 1]; arr[i + 1] = temp; swapped = true; } } } while (swapped); return arr; }
This step implements the sorting logic using nested loops. The outer do-while loop ensures that the sorting process continues until no swaps are made during a pass through the array.
Inside the loop, the for loop iterates through the array, comparing adjacent elements and swapping them if they are out of order. If a swap is made, the swapped variable is set to true.
Example Usage
Now, let's see how we can use the bubbleSort function to sort an array:
javascriptlet arr = [64, 34, 25, 12, 22, 11, 90]; bubbleSort(arr); console.log("Sorted array:", arr); // Output: Sorted array: [ 11, 12, 22, 25, 34, 64, 90 ]
Bubble Sort, while simple and intuitive, has limitations that restrict its practical usage in real-world scenarios. However, understanding Bubble Sort provides a foundational understanding of sorting algorithms, making it a valuable learning tool for aspiring programmers